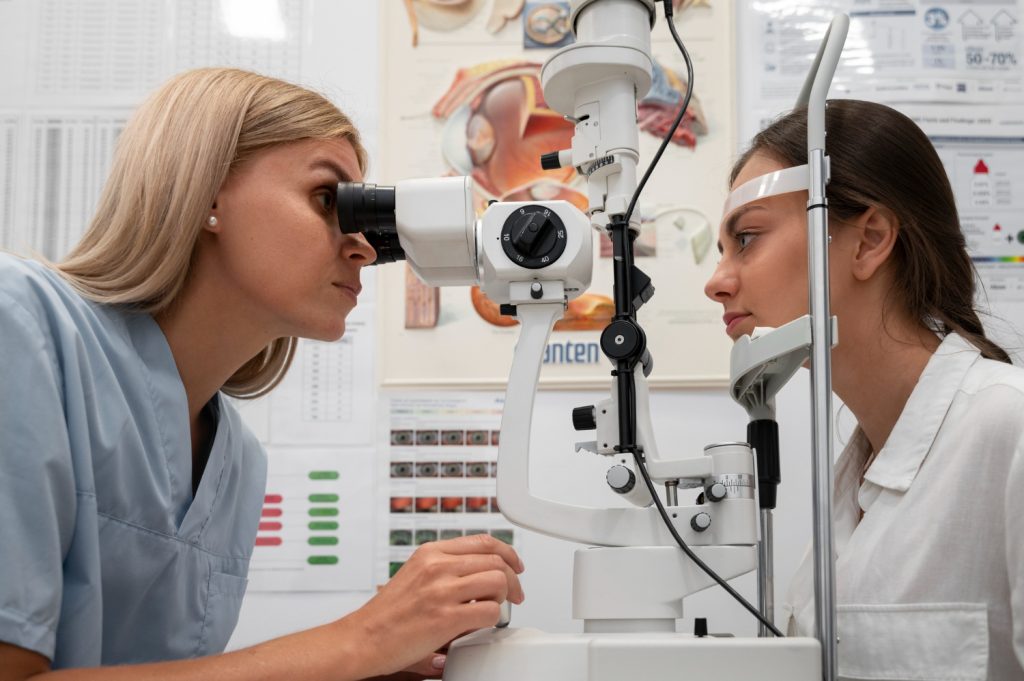
One of the most common eye health tests is dilated eye examination. It's a test that temporarily dilates the pupils of the eye to get a closer look at the retina and optic nerve. However, some people are concerned about the side effects of dilated eye exams, such as temporary glare and difficulty focusing. So, which fundus test can provide accurate results while allowing time for recovery?
Today, we'll look at the different ways in which glaucoma and retinal disease can be diagnosed with minimal side effects of dilated eye examination.
Table of Contents
Toggle
1. What is a pap smear?
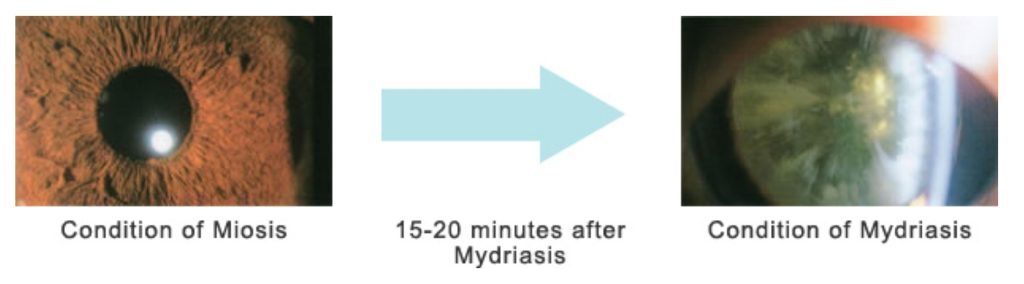
Source: Ikebukuro Sunshine Street Eye Clinic
1-1) Methods
A dilated fundus examination is a test in which the pupils are artificially dilated to get a closer look at the retina, optic nerve, and macula. It is essential for diagnosing retinal diseases such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy. It is difficult to fully observe the fundus when the pupil is constricted, so the test is performed after temporarily dilating the pupil by instilling a prokinetic agent, or pupil dilating eye drops. After the pupils have dilated sufficiently, the ophthalmologist will use an ophthalmoscope or fundus camera to look for abnormalities in the retina and optic nerve.
1-2) Time required
It takes about 20 to 30 minutes for the antidote to take full effect, and then 10 to 15 minutes for the test to proceed. Although the test is relatively safe, the anaesthetic may cause temporary anaesthetic side effects. These side effects can include difficulty focusing at close range or glare for a short period of time. Some people also experience a dry or stiff feeling in their eyes after using the antidote. These are temporary antidote side effects that usually go away on their own within a few hours.
1-3) Inspection intervals
Fundus exams are performed when retinal diseases such as glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and macular degeneration are suspected. In general, if you are over the age of 40 or have a family history of glaucoma or retinal disease, regular fundus exams may be recommended every one to two years. However, the frequency of testing may vary depending on the individual's eye health, and if you're at high risk, you may be advised to get tested more regularly depending on your condition.
2. What to do after an obstetric examination

Source: Freepik
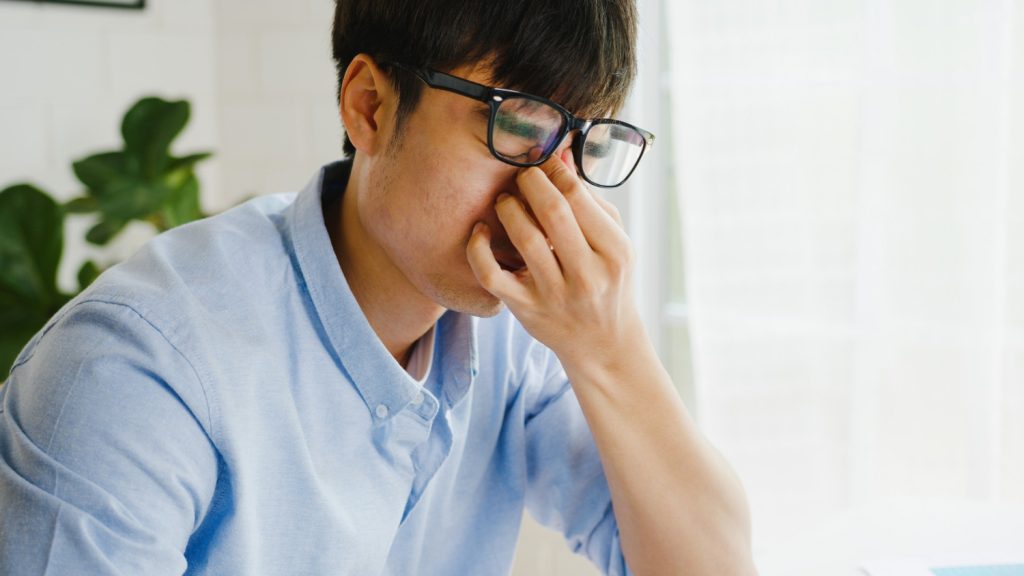
Because dilated pupils are used to examine the inside of the eye, you may experience visual changes for a period of time after the test. This is a temporary side effect of dilated pupils and should not be a cause for concern. The duration of symptoms after dilated pupils varies from person to person, but usually lasts between four and six hours and can affect some people for up to 24 hours. Being prepared and knowing what to expect after a dilated pupil test can help reduce discomfort.
2-1) Beware of blurred vision and glare
The first thing to watch out for after a dystocia is blurred vision and glare. You may have difficulty focusing at close range after the test, which can make the text appear blurry. Glare from bright lights can also increase, so it's a good idea to wear sunglasses when you're outdoors, so you can recover quickly from the test.
2-2) Avoid driving and precision work
The second thing to keep in mind after the test is that you should avoid driving or cycling. It is safe to avoid driving or riding a bicycle because your vision will not be clear after the test. You may also have difficulty with detailed documentation, so it is better to rest and prepare for recovery from the test rather than going back to work immediately.
2-3) Avoid rubbing or washing your eyes
During the dilated eye examination, you will be given eye drops, which may cause some discomfort after the examination. You should be careful not to rub your eyes at this time, as this can irritate the cornea. You should also be careful not to get water or cleaning products in your eyes when washing your face.
2-4) Consider eye care if symptoms persist after examination
Lastly, you may want to consider seeing an eye doctor for post-test care. If you experience extreme pain, blurred vision, or severe glare that persists after a day, you may need to see an ophthalmologist to help you recover from the test and manage any adverse effects on the fundus.
3. compare with the cost of an eye exam
Source: Homepage
The cost of an eye exam can vary depending on the type of exam, the provider, and whether or not you have health insurance coverage, so it's best to check with your healthcare provider to find out exactly how much your eye exam will cost. Here are some common eye exams and how much they cost.
3-1) Ocular optical coherence tomography (OCT)
Ophthalmic optical coherence tomography is a method of diagnosing diseases by obtaining cross-sectional images of the retina and optic nerve. The cost of this eye examination varies depending on the medical institution, but if you are covered by health insurance, you only need to pay 20% of the total cost. Therefore, the actual cost of the fundus examination is likely to be between 30,000 won and 60,000 won. However, the cost may vary depending on the hospital's size, location, and state-of-the-art equipment, so it is recommended that you contact the medical centre directly for the exact cost of the fundus examination.
3-2) Eye and orbital examination using ultrasound
Ophthalmological examinations use ultrasound to diagnose retinal diseases, glaucoma, and other conditions. Ultrasound examinations used to be expensive, but are now covered by health insurance. Currently, the out-of-pocket expenses range from 22,000 won (clinics) to 45,000 won (advanced general hospitals) on an outpatient basis. The cost of an eye examination may vary slightly depending on the medical institution.
3-3) Pre-cataract surgery instrumental examination
One of the most common methods of cataract detection is instrumentation, which uses ultrasound or laser interferometry to determine the number of intraocular lenses to be inserted after cataract surgery. On average, the cost of this eye examination ranges from 75,000 won to 123,000 won, but after health insurance is applied, the out-of-pocket expenses range from 20,000 won (clinics) to 41,000 won (high-end general hospitals). However, the cost of this fundus examination may vary from one medical centre to another, so it is recommended to check the exact cost.
How to Decide When to Have Cataract Surgery: Should You Do It Early?
4. the diagnosis of glaucomatous retinal disease is made at St Mary's Eye Hospital

Source: Homepage
Glaucoma and retinal diseases are conditions where early detection and appropriate treatment are critical. Early diagnosis through regular eye examinations is essential, especially as there are often no or minimal symptoms in the early stages. In addition, it is important to reduce the side effects of dilated eye examination and ensure eye health by using the best test method for your individual condition.
At St. Mary's Hospital Seoul, outpatient professors who specialise in retina use the latest eye examination equipment to accurately diagnose glaucoma and retinal diseases. In particular, St. Mary's offers a variety of diagnostic methods without the side effects of dilated eye examinations and focuses on patient convenience through customised examinations and treatment plans. Regular examinations and early diagnosis are crucial, as glaucoma and retinal diseases cannot be reversed once the optic nerve or retinal tissue has been damaged.
So, if you're in need of an eye examination for fundus disease, we encourage you to talk to your trusted eye care provider at St. Mary's and take control of your eye health.
Get a consultation at St. Mary's Ophthalmology - Go here
Phone number
02-577-7782
⏰Operating hours
Mon - Fri / AM 09:00 ~ PM 18:00
Saturday / AM 09:00 ~ PM 15:00
Lunch Break/PM 13:00 to PM 14:00
No Saturday lunch break








